This article was originally posted at Dinosaur Island.
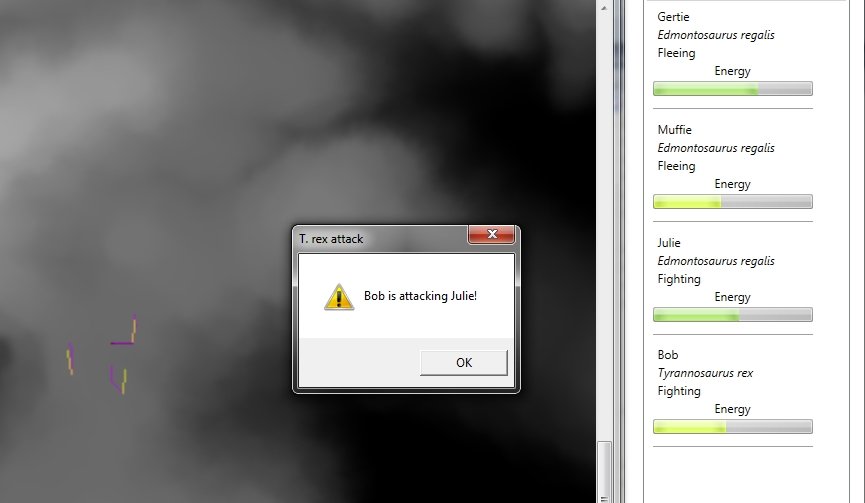
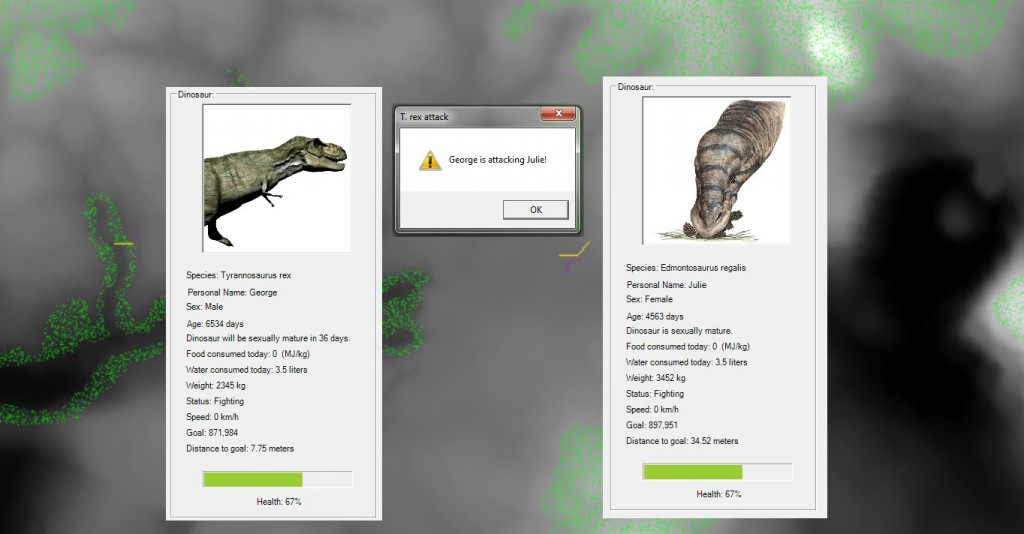
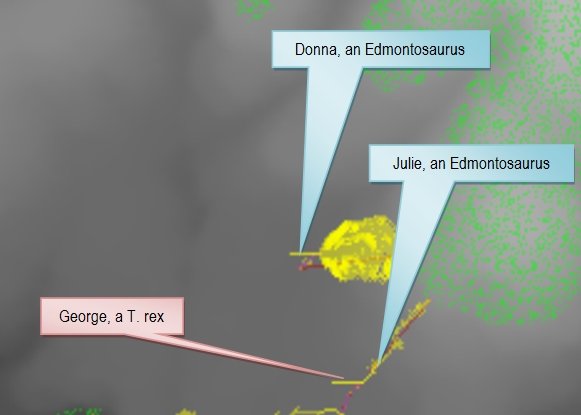
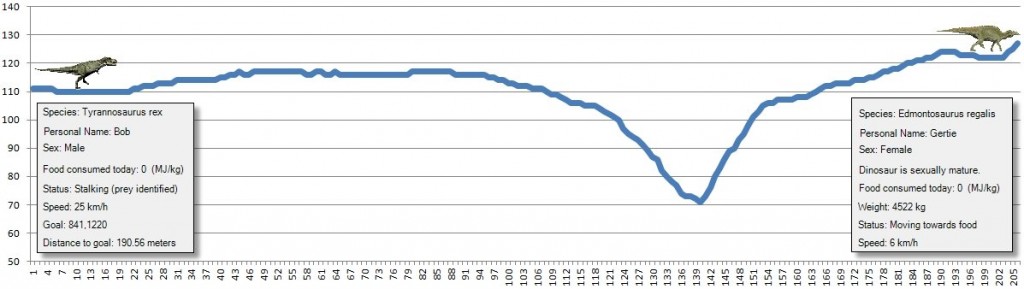
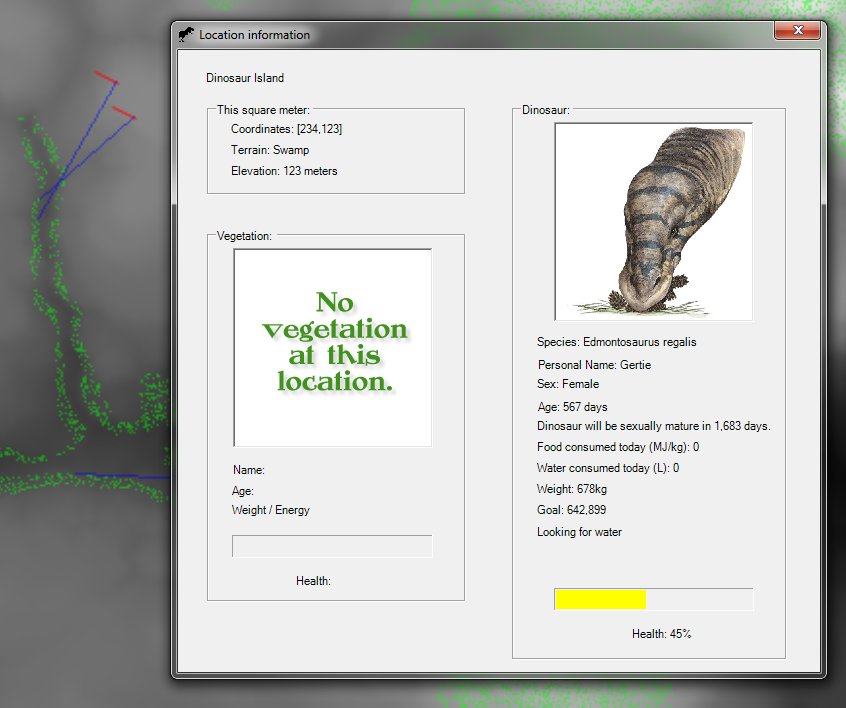
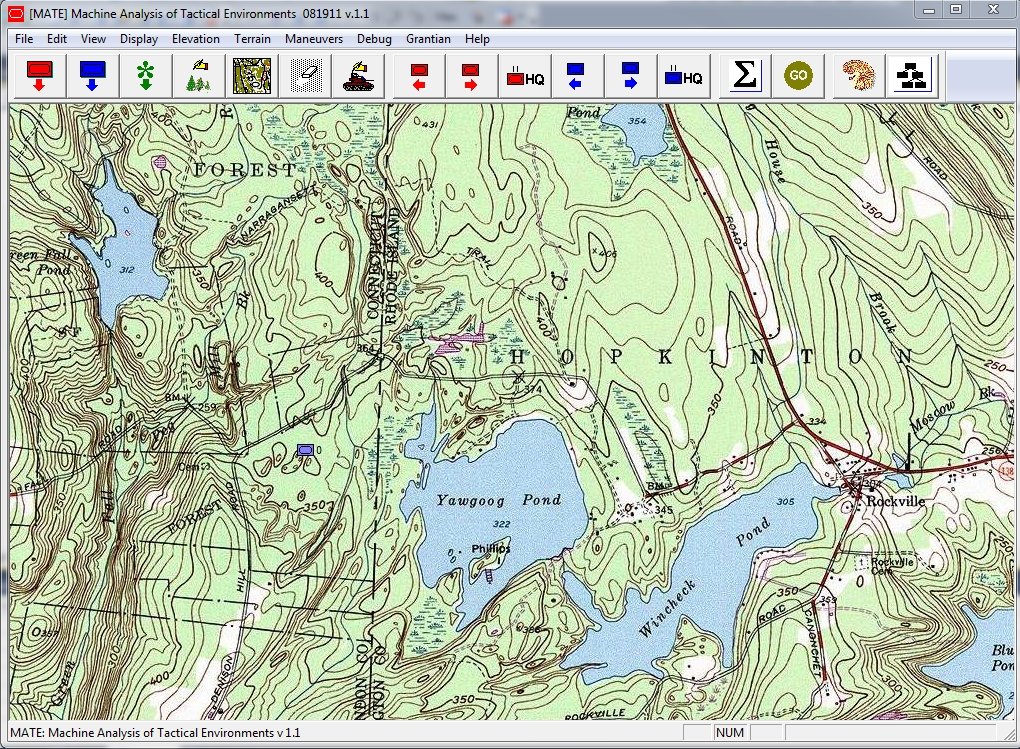
We are at the point in the development of the AI routines for the inhabitants of Dinosaur Island where it is time to make decisions about the combat models used to determine the resolution of hostile encounters. As shown in the screen capture of the Dinosaur Island AI testbed program (above), the simulation is placing the dinosaurs in various appropriate states such as: resting, eating, looking for food, looking for water, stalking prey, moving towards water, moving towards food, drinking, fighting and fleeing.
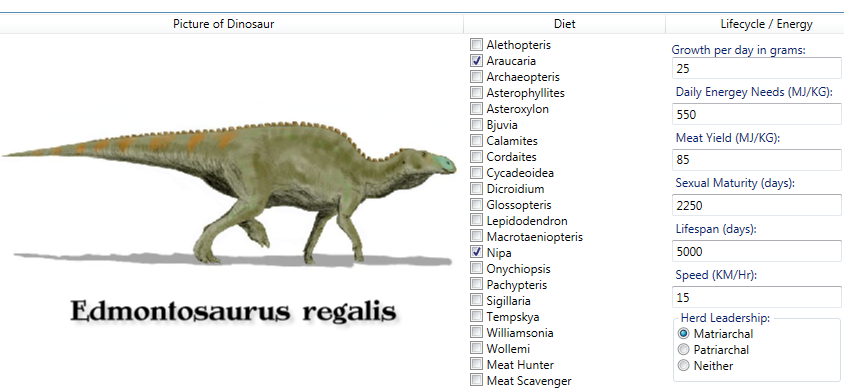
My first thought on the subject of modeling combat between T. rex and Edmontosaurus regalis, the first two resident species on the island, was that it would be handled similar to ‘melee combat’ models that I had previously used for my wargames.
Below is a page from the manual for UMS II: Nations at War explaining the 20 variable equation used to decide combat between tactical units.
I was envisioning something similar for Dinosaur Island until I happened to see this video (below) which includes a sequence (starting at 4:45) describing hypothetical Edmontosaurus and T. rex combat.
What I took away from the video was:
- Edmontosaurus regalis is bigger than I thought. I understood the size mathematically and that they could easily grow up to 13 meters (~ 40 feet) but it wasn’t until I saw this video that it was put in to perspective, “they were as big as a railroad car.” And, “they could look into a second story window.”
- The tail of an adult ‘bull’ Edmontosaurus regalis was a formidable weapon.
- T. rex, like many predators, would have preferred to attack adolescent or sick animals rather than encounter a full-size, and potentially lethal, ‘bull’.
- The correct pronunciation is Ed-MONT-o-saur-us. I’ve been saying it wrong for the last six months!
While there is still debate about whether T. rex was a predator or a scavenger (“Tyrannosaurus rex may have been an apex predator, preying upon hadrosaurs, ceratopsians, and possibly sauropods, although some experts have suggested it was primarily a scavenger. The debate over Tyrannosaurus as apex predator or scavenger is among the longest running in paleontology.” – Wikipedia) we know of at least once case where a T. rex tooth was found in an Edmontosaurus tail that had healed from the attack (“T. rex Tooth Crown Found Embedded in an Edmontosaurus Tail – Predatory Behaviour?” “The healed bone growth indicates that the duck-billed dinosaur survived this encounter. In February of this year, researchers from the University of Kansas and Florida reported on the discovery of evidence of a scar on fossilised skin tissue from just above the eye of an Edmontosaurus. In a paper, published in “Cretaceous Research”, the scientists concluded that this too was evidence of an attack of a T. rex on an Edmontosaurus.”). From this we can conclude that:
- Sometimes T. rex did attack a living Edmontosaurus.
- Sometimes the Edmontosaurus survived the attack.
Furthermore, we know that some T. rex had suffered bone injuries during their lifetime (“An injury to the right shoulder region of Sue resulted in a damaged shoulder blade, a torn tendon in the right arm, and three broken ribs. This damage subsequently healed (though one rib healed into two separate pieces), indicating Sue survived the incident.” – Wikipedia) consistent with the type of damage that a 5 meter long tail (described as being “like a baseball bat,” in the above, video) could inflict.
In other words, combat between T. rex and Edmontosaurus regalis was not a foregone conclusion. Indeed, it was entirely possible that the Edmontosaurus could walk away unscathed while the T. rex could suffer some broken bones.
The AI for Dinosaur Island will reflect this. When deciding if the T. rex will attack the AI will have to analyze the T. rex‘s chances of victory and potential injuries (risk versus reward) considering the size of the T. rex, the age of the T. rex, the health of the T. rex, the size of the prey, the age of the prey and the health of the prey. And, when the two dinosaurs actually engage in combat the tactics employed by both will probably decide the outcome.
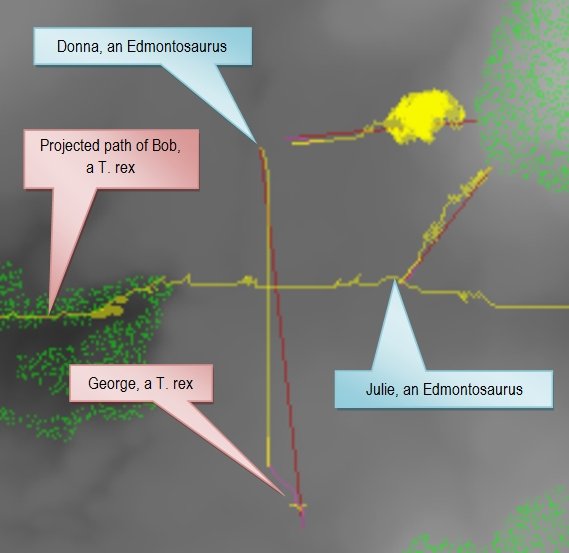
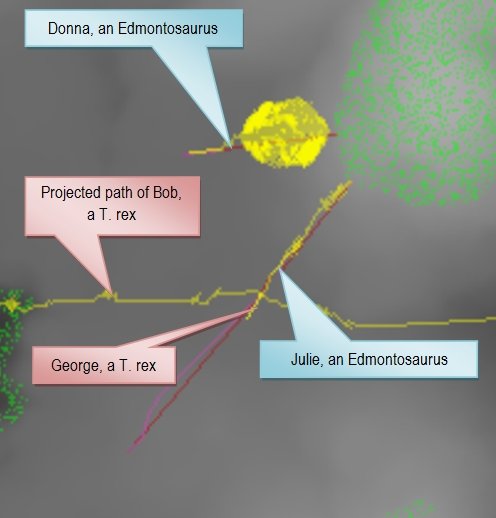
If the T. rex can sneak up on the Edmontosaurus until they are within 50 meters or less and then close the distance with a rush the advantage would certainly lie with the predator. If the Edmontosaurus has forewarning of the impending attack it would either attempt to flee or stand its ground and assume a defensive posture.
There is reason to believe that both Edmontosaurus and T. rex had well developed olfactory bulbs in their brains and smell was an important sense for both animals. We will add wind (and wind direction) to Dinosaur Island and incorporate this into the AI routines that control the dinosaurs. Predators will attempt to get ‘upwind’ of their prey; prey animals will ‘sniff’ the wind and respond if they smell a T. rex even if they can’t see it (see “Dinosaurs, tanks and line of sight algorithms” here).